java 判断字符串位置-字符串String类的特点及API记下方法,
字符串String类的特点
字符串的学习,有的同学就看看APIjava 判断字符串位置,记下方法,有的同学看看源代码,还有的同学画画图,自然学的深度是不一样的。
/**
* The {@code String} class represents character strings. All
* string literals in Java programs, such as {@code "abc"}, are
* implemented as instances of this class.
*
* Strings are constant; their values cannot be changed after they
* are created. String buffers support mutable strings.
* Because String objects are immutable they can be shared. For example:
*
* String str = "abc";
*
* is equivalent to:
*
* char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
* String str = new String(data);
*
* Here are some more examples of how strings can be used:
*
* System.out.println("abc");
* String cde = "cde";
* System.out.println("abc" + cde);
* String c = "abc".substring(2,3);
* String d = cde.substring(1, 2);
*
*
* The class {@code String} includes methods for examining
* individual characters of the sequence, for comparing strings, for
* searching strings, for extracting substrings, and for creating a
* copy of a string with all characters translated to uppercase or to
* lowercase. Case mapping is based on the Unicode Standard version
* specified by the {@link java.lang.Character Character} class.
*
* The Java language provides special support for the string
* concatenation operator ( + ), and for conversion of
* other objects to strings. String concatenation is implemented
* through the {@code StringBuilder}(or {@code StringBuffer})
* class and its {@code append} method.
* String conversions are implemented through the method
* {@code toString}, defined by {@code Object} and
* inherited by all classes in Java. For additional information on
* string concatenation and conversion, see Gosling, Joy, and Steele,
* The Java Language Specification.
String 类代表字符串。Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都作为此类的实例实现。
字符串是常量;它们的值在创建之后不能更改。字符串缓冲区支持可变的字符串。因为 String 对象是不可变的,所以可以共享。例如:
String str = "abc";
等效于:
char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str = new String(data);
下面给出了一些如何使用字符串的更多示例:
System.out.println("abc");
String cde = "cde";
System.out.println("abc" + cde);
String c = "abc".substring(2,3);
String d = cde.substring(1, 2);
String 类包括的方法可用于检查序列的单个字符、比较字符串、搜索字符串、提取子字符串、创建字符串副本并将所有字符全部转换为大写或小写。大小写映射基于 Character 类指定的 Unicode 标准版。
Java 语言提供对字符串串联符号("+")以及将其他对象转换为字符串的特殊支持。字符串串联是通过 StringBuilder(或 StringBuffer)类及其 append 方法实现的。字符串转换是通过 toString 方法实现的,该方法由 Object 类定义,并可被 Java 中的所有类继承。有关字符串串联和转换的更多信息,请参阅 Gosling、Joy 和 Steele 合著的 The Java Language Specification。
1、String是个final类
2、String是不可变的字符序列
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0 String对象的字符内容是存储在一个字符数组中的。
private意味着外面无法直接获取字符数组,而且String没有提供value的get和set方法,
final意味着字符数组的引用不可改变,即通过让value指向新的数组对象来实现修改String对象,
而且String也没有提供方法来修改value数组某个元素值,因此字符串的字符数组内容也不可变。
疑问?那么字符串的拼接、字符串的截取、字符串的替换等操作是如何实现的呢?
每次修改都创建一个新的char数组表示修改结果。
3、String对象的创建
String str = “hello”;
String s1 = new String(); // 本质上 this.value = new char[0];
String s2 = new String(String original); //this.value = original.value;
String s3 = new String(char[] a); //this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
String s4 = new String(char[] a,int startIndex,int count)
.......
4、字符串对象是如何存储的
字符串常量存储在字符串常量池,目的是共享
字符串非常量对象存储在堆中。
5、String的拼接
结论:
常量与常量的拼接结果在常量池
只要其中有一个是变量,结果就在堆中
如果拼接的结果调用intern()方法,就在常量池中
6、String对象的比较
==比较的是地址。
equals比较的是字符串的内容,重写了Object的equals方法。
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}String类的常用方法
1、常用方法系列之一
l int length():返回字符串的长度: return value.length;
l boolean isEmpty():判断是否是空字符串:return value.length == 0;
l String toLowerCase():使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写。
l String toUpperCase():使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。
l String trim():返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白。
l boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容
l boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString):与equals方法类似,忽略大小写
l String concat(String str):将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。 等价于用“+”
2、String类和字符相关操作
l char charAt(int index): 返回某索引处的字符return value[index];
l char[] toCharArray():将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组
l String(char[] value):分配一个新的 String,使其表示字符数组参数中当前包含的字符序列。
l String(char[] value, int offset, int count):分配一个新的 String,它包含取自字符数组参数一个子数组的字符。
3、String类字节与字符串操作方法
编码:把字符-->字节
l byte[] getBytes():使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
l byte[] getBytes(Charset charset) :使用给定的 charset 将此 String 编码到 byte 序列,并将结果存储到新的 byte 数组。
l byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) :使用指定的字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
解码:把字节-->字符
l String(byte[] bytes) :通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String。
l String(byte[] bytes, Charset charset):通过使用指定的 charset 解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String。
l String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) :通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 子数组,构造一个新的 String。
l String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, Charset charset):通过使用指定的 charset 解码指定的 byte 子数组,构造一个新的 String。
l String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, String charsetName):通过使用指定的字符集解码指定的 byte 子数组,构造一个新的 String。
l String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName):通过使用指定的 charset 解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String。
4、String类判断是否以指定内容开头或结尾
l boolean endsWith(String suffix):测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束。
l boolean startsWith(String prefix):测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始。
l boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset):测试此字符串从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定前缀开始。
5、String类字符串查找操作
l boolean contains(CharSequence s):当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列时,返回 true。
l int indexOf(int ch):返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
l int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):返回在此字符串中第一次出现指定字符处的索引,从指定的索引开始搜索。
l int indexOf(String str):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
l int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引java 判断字符串位置,从指定的索引开始。
l int lastIndexOf(int ch):返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引。
l int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索。
l int lastIndexOf(String str):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引。
l int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索。
indexOf和lastIndexOf方法如果未找到都是返回-1
6、String类字符串截取操作

l String substring(int beginIndex)
返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的从beginIndex开始截取到最后的一个子字符串。
l String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串从beginIndex开始截取到endIndex(不包含)的一个子字符串。
7、String类是否匹配正则
l boolean matches(String regex):告知此字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "12345";
//判断str字符串中是否全部有数字组成,即有1-n个数字组成
boolean matches = str.matches("\\d+");
System.out.println(matches);
String tel = "0571-4534289";
//判断这是否是一个杭州的固定电话
boolean result = tel.matches("0571-\\d{7,8}");
System.out.println(result);
}8、String类替换操作
l String replace(char oldChar, char newChar):
返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的。
l String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement):
使用指定的字面值替换序列替换此字符串所有匹配字面值目标序列的子字符串。
l String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement):
使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。
l String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement):
使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串匹配给定的正则表达式的第一个子字符串。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "12hello34world5java7891mysql456";
//把字符串中的数字替换成,,如果结果中开头和结尾有,的话去掉
String string = str.replaceAll("\\d+", ",").replaceAll("^,|,#34;, "");
System.out.println(string);
}9、String类字符串拆分操作
l String[] split(String regex):根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串。
l String[] split(String regex, int limit):根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分此字符串,最多不超过limit个,如果超过了,剩下的全部都放到最后一个元素中。
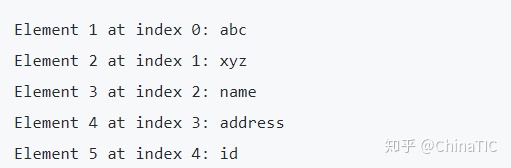
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello|world|java";
String[] strings = str.split("\\|");
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string);
}
String str2 = "hello.world.java";
String[] strings2 = str2.split("\\.");
for (String string : strings2) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}往期精彩内容:
Java常用类_包装类Wrapper
Java开发中常用的消息队列工具 ActiveMQ
html中的元素类型种类及特点
使用QueryRunner类实现更新
英语不好照样可以搞定Java编程—Java常用英语汇总


 上一篇
上一篇 







