python全局命名空间-python 命名风格
Python-函数基础总结与内置函数
1.
def plus(*args):
return sum(args)
print(plus(1, 2, 3))
print(plus(2, 4, 6, 8, 10))
结果:
6
30
2.
def power(x=2, n):
return x ** n
结果:
def power(x=2, n):
^
SyntaxError: non-default argument follows default argument
注意:有默认值的参数必须在无默认值参数的后面
可写为:
def power(n, x=2):
return x ** n
对于包含 参数有默认值的 函数python全局命名空间,而且已经调用了,不易改动,不方便添加不含默认值的参数,保证健壮性,只能添加默认值。
power(x,n=2)添加y参数时power(x,n=2,y)是不对的,只能是power(x,n=2,y=None),y可以赋值为其他默认值。
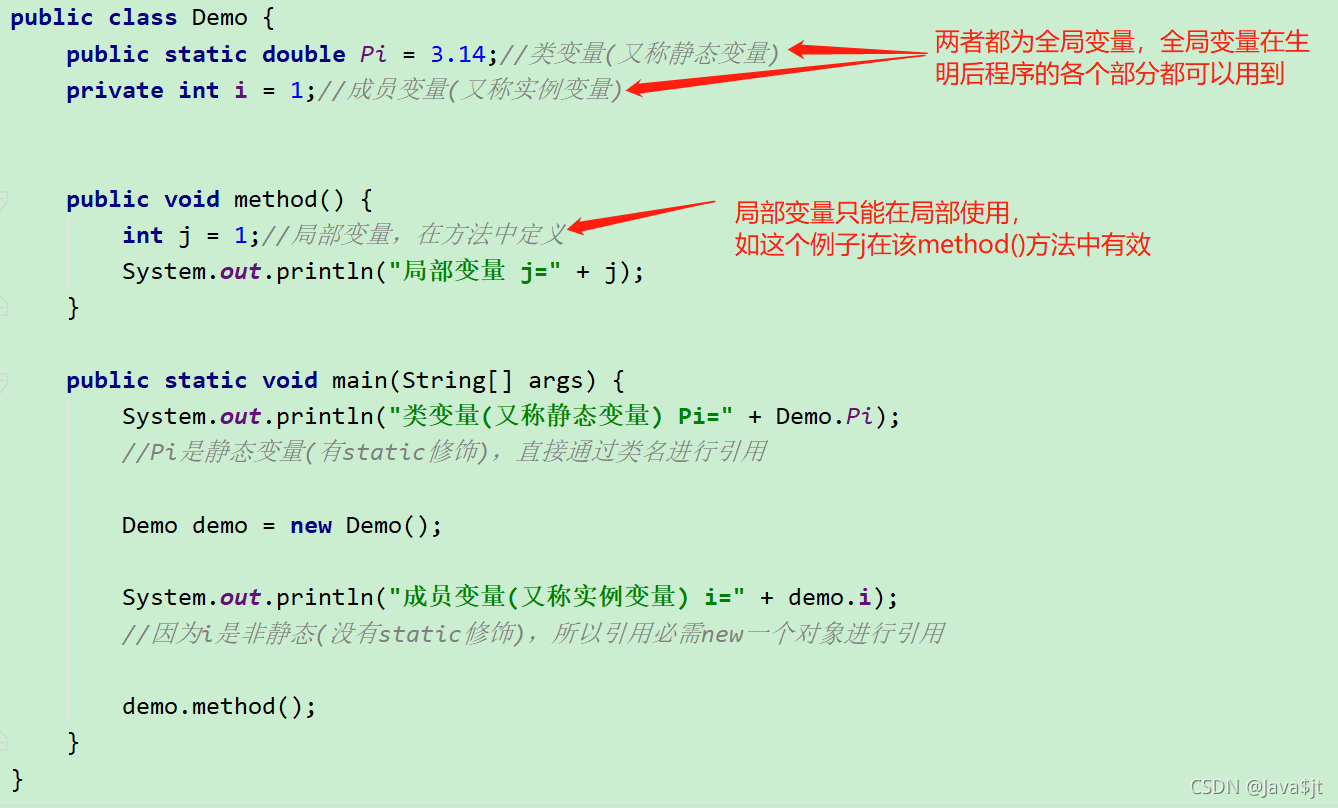
命名空间
命名空间(namespace )是一个从名字到对象的映射,当前,大部分命名空间都由 Python 字典实现。
同命名空间中的名称之间绝对没有关系,例如,两个不同的模块都可以定义一个 maximize 函数而不会产生混淆,当然,模块的用户必须在其前面加上模块名称。类似一个文件夹内不能有重复名称的文件,但是,不同的文件夹内可以有相同名称的文件。
在不同时刻创建的命名空间拥有不同的生存期。包含内置名称的命名空间是在 Python 解释器启动时创建的python全局命名空间,永远不会被删除。
模块的全局命名空间在模块定义被读入时创建,通常,模块命名空间也会持续到解释器退出。
作用域
一个 作用域 是一个命名空间可直接访问的 Python 程序的文本区域。 这里的 “可直接访问” 意味着对名称的非限定引用(非限定引用就是你没加关键字,Python默认情况下)会尝试在命名空间中查找名称。
搜索顺序:L –> E –> G –>B
接下来我们就不说B了,随时都能访问,应该没有什么疑惑。
全局变量与局部变量
我们定义一个全局变量name,Show函数中定义一个局部变量name。
name = 'lady_killer'

def Show():
university = 'BUPT'
def show_nonlocal():
print('show_nonlocal:', university)
print('show_nonlocal:', name)
def show_global():
print('show_global:', university)
print('show_global:', name)
show_nonlocal()
show_global()
print('local:', university)
# NameError: name 'university' is not defined
# print(university)
Show()
print('gloabal:', name)结果:
show_nonlocal: BUPT
show_nonlocal: lady_killer
show_global: BUPT
show_global: lady_killer
local: BUPT
gloabal: lady_killer
当然,局部作用域外不能访问局部变量
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "learnarea.py", line 28, in
print(university)
NameError: name 'university' is not defined
就近原则
接下来我们就看看同名的情况。
我们对show函数进行一下修改,在局部作用域增加同名的变量。

def Show():
university = 'BUPT'
name = 'YuBo'
def show_nonlocal():
university = 'bupt'
name = 'frankyu'
print('show_nonlocal:', university)
print('show_nonlocal:', name)
def show_global():
print('show_global:', university)
print('show_global:', name)
show_nonlocal()
show_global()
print('local:', university)结果:
show_nonlocal: bupt
show_nonlocal: frankyu
show_global: BUPT
show_global: YuBo
local: BUPT
gloabal: lady_killer
可以看到按照L->E->G顺序查找,即就近原则。
只读问题
我们尝试增加一个全局变量num,并在函数内进行复合的赋值操作,关于操作符可查看。
num = 1
def Show():
university = 'BUPT'
name = 'YuBo'
# UnboundLocalError: local variable 'num' referenced before assignment
num += 1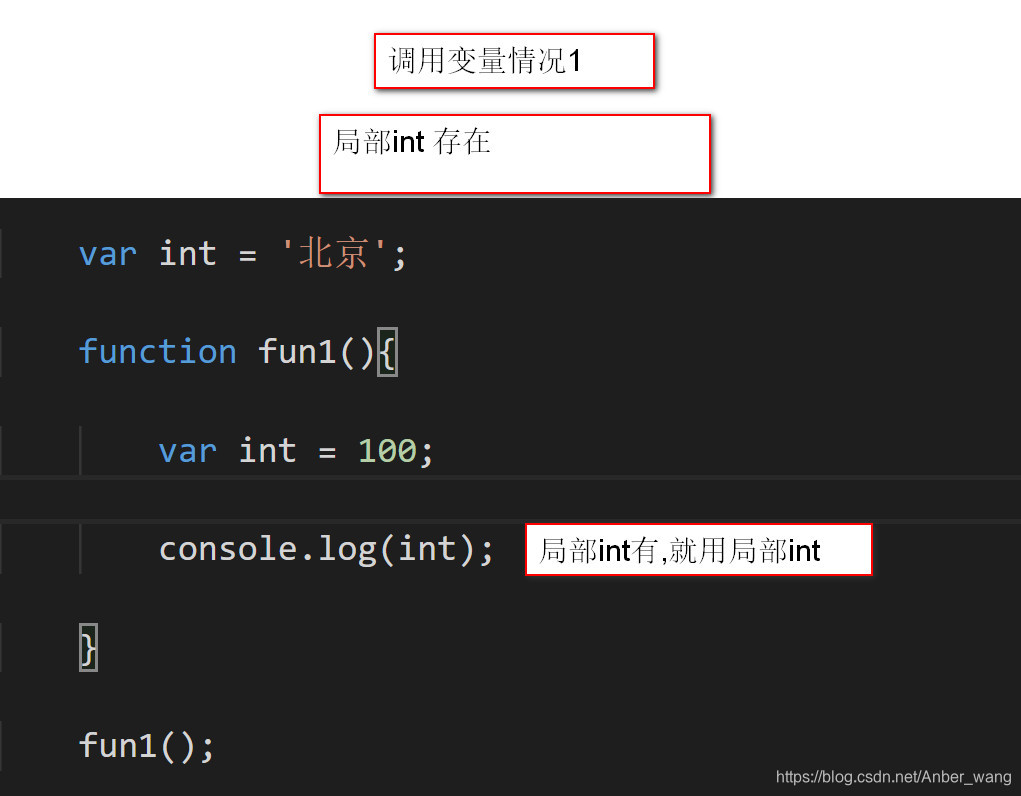
结果:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "learnarea.py", line 35, in
Show()
File "learnarea.py", line 16, in Show
num += 1
UnboundLocalError: local variable 'num' referenced before assignment
num += 1,即 num = num + 1,在找后面的num时没有去全局变量寻找,而是认为局部变量,但是我们没有定义局部变量num,所以就是赋值前引用,如果我们在num+=1前使用num=2之类的进行定义num,就不会出错了,但如果我们想使用全局变量该怎么办呢?请继续看。
关键字
global关键字用于使用全局变量
nonlocal关键字用于使用嵌套外部函数变量
def Show():
university = 'BUPT'
global name
name += 'YuBo'
# UnboundLocalError: local variable 'num' referenced before assignment
# num += 1
def show_nonlocal():
nonlocal university
university += 'bupt'
name = 'frankyu'
print('show_nonlocal:', university)
print('show_nonlocal:', name)
def show_global():
print('show_global:', university)
print('show_global:', name)结果:
show_nonlocal: BUPTbupt
show_nonlocal: frankyu
show_global: BUPTbupt
show_global: lady_killerYuBo
local: BUPTbupt
gloabal: lady_killerYuBo
全部代码
"""
--coding:utf-8--
@File: learnarea.py
@Author:frank yu
@DateTime: 2020.10.23 15:00
@Contact: frankyu112058@gmail.com
@Description: 学习变量作用域
"""
name = 'lady_killer'
num = 1
def Show():
university = 'BUPT'
global name
name += 'YuBo'
# UnboundLocalError: local variable 'num' referenced before assignment
# num += 1
def show_nonlocal():
nonlocal university
university += 'bupt'
name = 'frankyu'
print('show_nonlocal:', university)
print('show_nonlocal:', name)
def show_global():
print('show_global:', university)
print('show_global:', name)
show_nonlocal()
show_global()
print('local:', university)

# NameError: name 'university' is not defined
# print(university)
Show()
print('gloabal:', name)
总结 思考题
以下代码。结果是什么?
send_packet = 56
def test(i):
global send_packet
if i > 5:
send_packet = 1
return send_packet
print(test(2))
print(test(6))如果是这样呢?
send_packet = 56
def test(i):
global send_packet
if i > 5:
send_packet = 1
return send_packet
print(test(6))
print(test(2))答案见:Python-面向对象编程总结(类、对象、派生、继承、方法、内置函数等)
更多python相关内容:【python总结】python学习框架梳理
本人b站账号:lady_killer9


 上一篇
上一篇 








