java 数据库连接池-java数据池
每天早上七点三十,准时推送干货 一、介绍
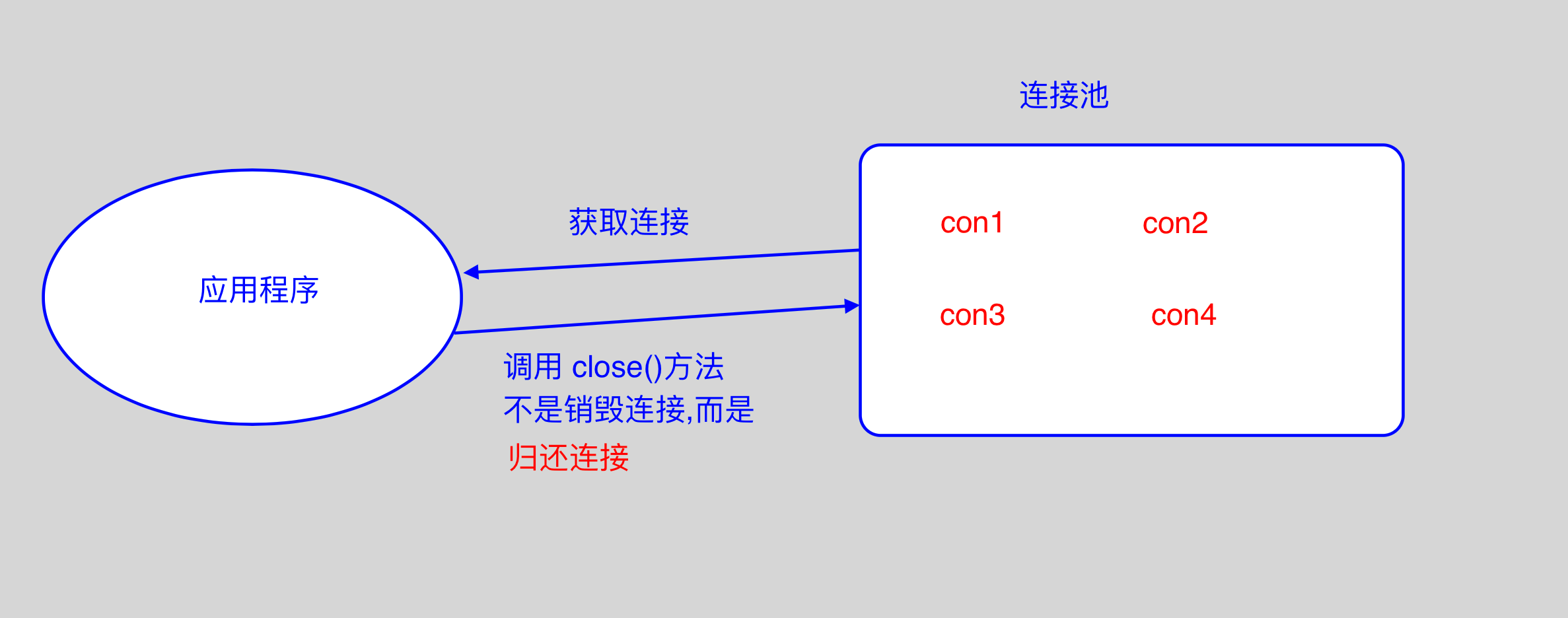
数据库连接是一项非常关键的、有限的、昂贵的资源,这一点在多用户的网页应用程序中体现得尤为突出。
记得之前做的一个项目,当时的应用程序配置的c3p0数据库连接池,最大允许的连接数是500,结果上线没多久,并发量直接上来了,导致大量的数据插入失败,当晚的心情可想而知~
从那一次事故之后,让我对应用程序的数据库连接数有了一次深刻的认识,为了防止再次栽跟头,特意抽了一个时间来编写程序测试案例,用于测试各个数据源连接池的稳定性,以防止自己再次踩坑!
话不多说,直接撸起来!
二、程序实例
熟悉 web 系统开发的同学,基本都知道,在 Java 生态中开源的常用数据库连接池有以下几种:
dbcp: DBCP是一个依赖Jakarta commons-pool对象池机制的数据库连接池,DBCP可以直接的在应用程序中使用,Tomcat的数据源使用的就是DBCPc3p0: c3p0是一个开放源代码的JDBC连接池,它在lib目录中与Hibernate一起发布,包括了实现jdbc3和jdbc2扩展规范说明的Connection和Statement池的DataSources对象druid:阿里出品,淘宝和支付宝专用数据库连接池,但它不仅仅是一个数据库连接池,它还包含一个 ProxyDriver,一系列内置的JDBC组件库,一个SQL Parser。支持所有JDBC兼容的数据库,包括Oracle、MySql、Derby、Postgresql、SQL Server、H2等等。今天我们就一起来对比一下,这三种数据源连接池的稳定性。
2.1、创建测试表
下面以 mysql 数据库为例,首先创建一个
t_test表,方面后续进行插入数据操作。CREATE TABLE t_test (
id bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '名称',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB COMMENT='测试表';2.2、 编写测试用例
以dbcp为例,首先创建一个dbcp-jdbc.properties配置文件。
username=root
password=Hello@123456
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.200:3306/testdb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
initialSize=5
maxActive=1000
maxIdle=5
removeAbandoned=ture
removeAbandonedTimeout=20
logAbandoned=true
maxWait=100接着,创建一个连接池工具DbcpJdbcUtil。
public class DbcpJdbcUtil {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DbcpJdbcUtil.class);
/**jdbc配置文件*/
private static Properties prop = new Properties();
private static BasicDataSource dataSource = null;
// 它是事务专用连接!
private static ThreadLocaltl = new ThreadLocal ();
static {
classPathSourceRead();
}
private static void classPathSourceRead(){
//读取指定位置的配置文档(读取class目录文件)
try {
logger.info("jdbc路径:" + SysConstants.getValue());
prop.load(DbcpJdbcUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(SysConstants.getValue()));
logger.info("数据配置信息" + JSON.toJSONString(prop));
logger.info("初始化默认jdbc配置文件成功!");
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("初始化默认jdbc文件失败!",e);
}
}
/**
* 从连接池获取数据源
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static BasicDataSource getDataSource() throws Exception {
try {
if (dataSource == null) {
synchronized (DbcpJdbcUtil.class) {
if (dataSource == null) {
dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setUsername(prop.getProperty("username"));
dataSource.setPassword(prop.getProperty("password"));
dataSource.setDriverClassName(prop.getProperty("driverClassName"));
dataSource.setUrl(prop.getProperty("url"));
dataSource.setInitialSize(Integer.valueOf(prop.getProperty("initialSize")));
dataSource.setMaxActive(Integer.valueOf(prop.getProperty("maxActive")));
dataSource.setMaxIdle(Integer.valueOf(prop.getProperty("maxIdle")));
dataSource.setRemoveAbandoned(Boolean.valueOf(prop.getProperty("removeAbandoned")));
dataSource.setRemoveAbandonedTimeout(Integer.valueOf(prop.getProperty("removeAbandonedTimeout")));
dataSource.setLogAbandoned(Boolean.valueOf(prop.getProperty("logAbandoned")));
dataSource.setMaxWait(Integer.valueOf(prop.getProperty("maxWait")));
}
}
}
return dataSource;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("根据数据库名称获取数据库资源失败," , e);
throw new Exception("根据数据库名称获取数据库资源失败");
}
}
/**
* 使用连接池返回一个连接对象
*
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
try {
Connection con = tl.get();
// 当con不等于null,说明已经调用过beginTransaction(),表示开启了事务!
if (con != null)
return con;
return getDataSource().getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("获取数据库连接失败!", e);
throw new SQLException("获取数据库连接失败!");
}
}
/**
* 开启事务 1. 获取一个Connection,设置它的setAutoComnmit(false)
* 2. 还要保证dao中使用的连接是我们刚刚创建的! --------------
* 3. 创建一个Connection,设置为手动提交
* 4. 把这个Connection给dao用!
* 5. 还要让commitTransaction或rollbackTransaction可以获取到!
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void beginTransaction() throws Exception {
try {
Connection con = tl.get();
if (con != null) {
con.close();
tl.remove();
//throw new SQLException("已经开启了事务,就不要重复开启了!");
}
con = getConnection();
con.setAutoCommit(false);
tl.set(con);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("数据库事物开启失败!", e);
throw new SQLException("数据库事物开启失败!");
}
}
/**
* 提交事务 1. 获取beginTransaction提供的Connection,然后调用commit方法
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void commitTransaction() throws SQLException {
Connection con = tl.get();
try {
if (con == null)
throw new SQLException("还没有开启事务,不能提交!");
con.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("数据库事物提交失败!", e);
throw new SQLException("数据库事物提交失败!");
} finally {
if (con != null) {
con.close();
}
tl.remove();
}
}
/**
* 回滚事务 1. 获取beginTransaction提供的Connection,然后调用rollback方法
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void rollbackTransaction() throws SQLException {
Connection con = tl.get();
try {
if (con == null)
throw new SQLException("还没有开启事务,不能回滚!");
con.rollback();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("数据库事物回滚失败!", e);
throw new SQLException("数据库事物回滚失败!");
} finally {
if (con != null) {
con.close();
}
tl.remove();
}
}
/**
* 释放连接
* @param connection
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void releaseConnection(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
try {
Connection con = tl.get();
// 判断它是不是事务专用,如果是,就不关闭! 如果不是事务专用,那么就要关闭!
// 如果con == null,说明现在没有事务,那么connection一定不是事务专用的!
//如果con != null,说明有事务,那么需要判断参数连接是否与con相等,若不等,说明参数连接不是事务专用连接
if (con == null || con != connection)
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("数据库连接释放失败!", e);
throw new SQLException("数据库连接释放失败!");
}
}
}最后,编写单元测试程序DBCPTest。
public class DBCPTest {
private static final int sumCount = 1000000;
private static final int threadNum = 600;
private void before(String path) {
SysConstants.putValue(path);
new DBCPService().insert("delete from t_test");
}
@Test
public void testMysql() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = "config/mysql/dbcp-jdbc.properties";
before(path);
for (int i =0; i < 1; i++) {
String sql = "insert into t_test(id,name) values('" +i+ "','dbcp-mysql-" + i + "')";
new DBCPService().insert(sql);
}
System.out.println("耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
@Test
public void testThreadMysql() throws InterruptedException {
String path = "config/mysql/dbcp-jdbc.properties";
before(path);
BlockingQueuequeue = new LinkedBlockingQueue ();
for (int i = 0; i < sumCount; i++) {
String sql = "insert into t_test(id,name) values('" +i+ "','dbcp-mysql-" + i + "')";
queue.put(sql);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadNum);
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
final int finalI = i + 1;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread " + finalI + " start");
boolean isGo = true;
while (isGo) {
String sql = queue.poll();
if(sql != null) {
new DBCPService().insert(sql);
}else {
isGo =false;
System.out.println("thread " + finalI + " finish");
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}c3p0、druid的配置也类似,这里就不在重复介绍了!
三、性能测试
程序编写完成之后,下面我们就一起来结合各种不同的场景来测试一下各个数据连接池的表现。
为了进一步扩大测试范围,本次测试还将各个主流的数据库也拉入进去,测试的数据库分别是:mysql-5.7、oracle-12、postgresql-9.6
3.1、插入10万条数据
首先,我们来测试一下,各个数据库插入10万条数据,采用不同的数据源连接池,看看它们的表现如何?
从上面测试结果,我们可以基本得出如下结论:
其中druid对postgresql的支持性能最好,c3p0的表现比较差!
3.2、插入100万条数据
可能有的同学,还不太认可,下面我们就来测试一下插入100万条,看看它们的表现如何?
从上面测试结果,我们可以基本得出如下结论:
还是一样的结论,druid对postgresql的支持性能最好,c3p0的表现比较差!
四、小结
从上面的测试结果,我们可以很清晰的看到,在数据连接池方面,druid和dbcp旗鼓相当,而并发方面druid的稳定性大于dbcp,c3p0相比druid和dbcp,稳定性和执行速度要弱些。
在数据库方面,postgresql速度要优于oraclejava 数据库连接池,而oracle对各个数据源的支持和稳定性要有优势,mysql相比oracle和postgresqljava 数据库连接池,执行速度要弱些。
如果在实际开发中,数据源连接池推荐采用druid,数据库的选用方面 postgresql > oracle > mysql。
本次测试的数据全部都是真实的,希望能帮到大家,喜欢就帮忙点个赞吧





 上一篇
上一篇 








