java 写入大量文件到磁盘-java将字符串写入文件
发布时间:2023-03-30 07:03 浏览次数:次 作者:佚名
Java文件写入的6种方法
2022-12-08Java
写程序时经常会碰到读写文件的场景,在java中操作文件的方法本质上只有两种:字符流和字节流,而他们的实现类又有很多,因此,有时候用起来java 写入大量文件到磁盘,就会比较乱。
这篇文章系统介绍了java操作文件的几种方式,学习一下,
filewriter类的实现如下java 写入大量文件到磁盘,
/**
* 方法 1:使用 filewriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static void filewritermethod(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (filewriter filewriter = new filewriter(filepath)) {
filewriter.append(content);
}
}
只需要传入具体的文件路径和待写入的内容即可,调用代码如下,
public static void main(string[] args) {
filewritermethod("/users/mac/downloads/io_test/write1.txt", "hello, java.");
}了解了缓存区的优点之后,咱们回到本文的主题,接下来我们用bufferedwriter来文件的写入,实现代码如下,

/**
* 方法 2:使用 bufferedwriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static void bufferedwritermethod(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (bufferedwriter bufferedwriter = new bufferedwriter(new filewriter(filepath))) {
bufferedwriter.write(content);
}
}/**
* 方法 3:使用 printwriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static void printwritermethod(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (printwriter printwriter = new printwriter(new filewriter(filepath))) {
printwriter.print(content);
}
}/**
* 方法 4:使用 fileoutputstream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static void fileoutputstreammethod(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (fileoutputstream fileoutputstream = new fileoutputstream(filepath)) {
byte[] bytes = content.getbytes();
fileoutputstream.write(bytes);
}
}/**
* 方法 5:使用 bufferedoutputstream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static void bufferedoutputstreammethod(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (bufferedoutputstream bufferedoutputstream = new bufferedoutputstream(
new fileoutputstream(filepath))) {
bufferedoutputstream.write(content.getbytes());
}
}/**
* 方法 6:使用 files 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static void filestest(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
files.write(paths.get(filepath), content.getbytes());
}import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.files;
import java.nio.file.paths;
public class writeexample {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception {
// 构建写入内容
stringbuilder stringbuilder = new stringbuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
stringbuilder.append("abcdefghigklmnopqrseuvwxyz");
}
// 写入内容
final string content = stringbuilder.tostring();
// 存放文件的目录
final string filepath1 = "/users/mac/downloads/io_test/write1.txt";
final string filepath2 = "/users/mac/downloads/io_test/write2.txt";
final string filepath3 = "/users/mac/downloads/io_test/write3.txt";
final string filepath4 = "/users/mac/downloads/io_test/write4.txt";
final string filepath5 = "/users/mac/downloads/io_test/write5.txt";
final string filepath6 = "/users/mac/downloads/io_test/write6.txt";
// 方法一:使用 filewriter 写文件
long stime1 = system.currenttimemillis();
filewritertest(filepath1, content);
long etime1 = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("filewriter 写入用时:" + (etime1 - stime1));
// 方法二:使用 bufferedwriter 写文件
long stime2 = system.currenttimemillis();
bufferedwritertest(filepath2, content);
long etime2 = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("bufferedwriter 写入用时:" + (etime2 - stime2));
// 方法三:使用 printwriter 写文件
long stime3 = system.currenttimemillis();
printwritertest(filepath3, content);
long etime3 = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("printwritertest 写入用时:" + (etime3 - stime3));
// 方法四:使用 fileoutputstream 写文件
long stime4 = system.currenttimemillis();
fileoutputstreamtest(filepath4, content);
long etime4 = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("fileoutputstream 写入用时:" + (etime4 - stime4));
// 方法五:使用 bufferedoutputstream 写文件
long stime5 = system.currenttimemillis();
bufferedoutputstreamtest(filepath5, content);
long etime5 = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("bufferedoutputstream 写入用时:" + (etime5 - stime5));
// 方法六:使用 files 写文件
long stime6 = system.currenttimemillis();
filestest(filepath6, content);
long etime6 = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("files 写入用时:" + (etime6 - stime6));
}
/**
* 方法六:使用 files 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
private static void filestest(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
files.write(paths.get(filepath), content.getbytes());
}
/**
* 方法五:使用 bufferedoutputstream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
private static void bufferedoutputstreamtest(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (bufferedoutputstream bufferedoutputstream = new bufferedoutputstream(
new fileoutputstream(filepath))) {
bufferedoutputstream.write(content.getbytes());
}
}
/**
* 方法四:使用 fileoutputstream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
private static void fileoutputstreamtest(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (fileoutputstream fileoutputstream = new fileoutputstream(filepath)) {
byte[] bytes = content.getbytes();
fileoutputstream.write(bytes);
}
}
/**
* 方法三:使用 printwriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
private static void printwritertest(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (printwriter printwriter = new printwriter(new filewriter(filepath))) {
printwriter.print(content);
}
}
/**
* 方法二:使用 bufferedwriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
private static void bufferedwritertest(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (bufferedwriter bufferedwriter = new bufferedwriter(new filewriter(filepath))) {
bufferedwriter.write(content);
}
}
/**
* 方法一:使用 filewriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws ioexception
*/
private static void filewritertest(string filepath, string content) throws ioexception {
try (filewriter filewriter = new filewriter(filepath)) {
filewriter.append(content);
}
}
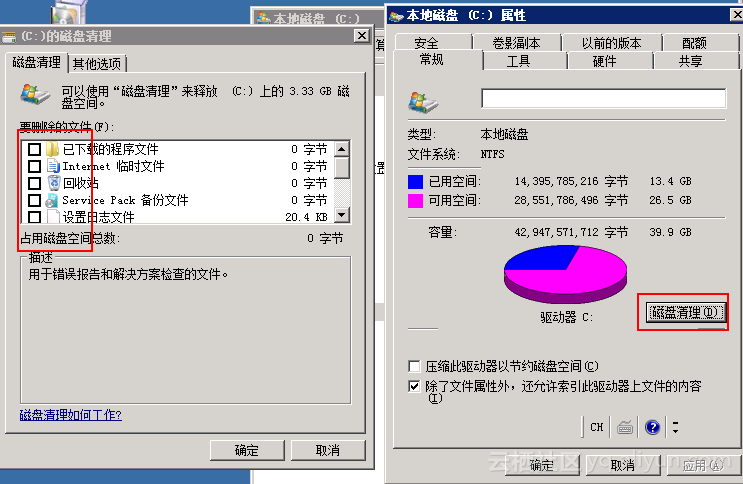
}在查看结果之前,我们先去对应的文件夹看看写入的文件是否正常,如下图所示,
从上述结果可以看出,每种方法都正常写入了26 mb的数据,他们最终执行的结果如下图所示,



 上一篇
上一篇 








